Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources: Hello, fantastic readers! Today, let’s delve into the world of Vitamin E—an essential fat-soluble vitamin crucial for our well-being. Our primary focus will be on the valuable insights shared by Well Health Organic, specifically in their comprehensive article titled “Vitamin E Health Benefits and Nutritional Sources” found at Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources.
Vitamin E: The Antioxidant Shield
Vitamin E, in its alpha-tocopherol form, is the body’s preferred variant, acting as a potent antioxidant. Its role involves neutralizing free radicals, those mischievous agents capable of wreaking havoc on our cells. The scientific community first highlighted the significance of antioxidant vitamins, including Vitamin E, in the 1980s. Researchers discovered a connection between free radical damage and the development of atherosclerosis, a condition leading to artery blockage. While Vitamin E exhibits potential in preventing free radical formation and protecting cells from damage, conflicting study results have somewhat tempered the enthusiasm for using high doses to ward off chronic diseases.
Nutritional Sources of Vitamin E
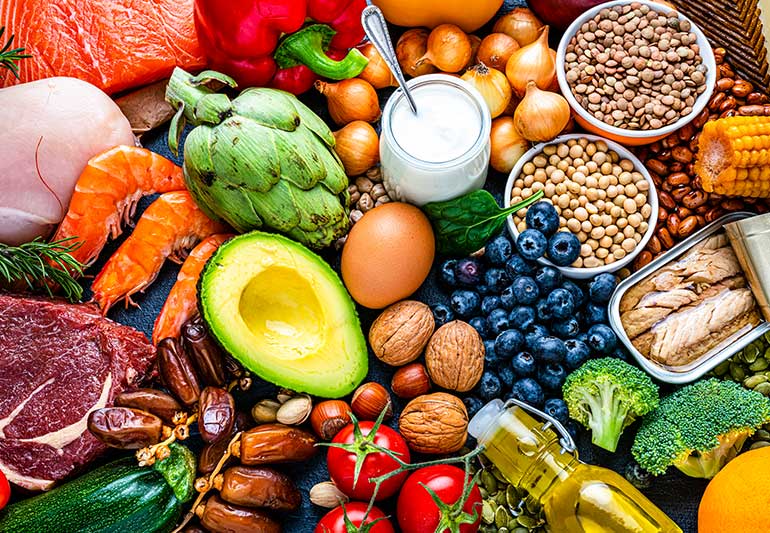
A balanced diet can ensure ample Vitamin E intake, as it is abundantly present in various foods. Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources emphasizes the following sources:
- Wheat germ oil
- Oils from soybean, safflower, and sunflower
- Sunflower seeds
- Nuts (peanuts, almonds) and peanut butter
- Leafy greens (beet greens, collard greens, spinach)
- Pumpkin
- Red bell pepper
- Asparagus
- Mangoes
- Avocados
Also Read : Wellhealthorganic.com know the causes of white hair and easy ways to prevent it naturally
Detecting Vitamin E Deficiency
Given its prevalence in foods and supplements, Vitamin E deficiency is rare. However, individuals with digestive issues or conditions hindering fat absorption, such as pancreatitis or celiac disease, may be at risk. Signs of deficiency, according to Wellhealthorganic.com, include retinopathy, peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, and impaired immune function.
Health Benefits Unveiled
Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources points out several health benefits attributed to Vitamin E:
- Reduced risk factors for heart diseases, including high cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Improved lung health and diminished asthmatic symptoms in children and adults.
- Alleviation of menstrual cramps and pelvic pain in women with dysmenorrhea or endometriosis.
- Potential aid in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Protection against cognitive decline.
- Anti-inflammatory effects and strengthened immune system in older adults.
Navigating Vitamin E Safety
Addressing concerns about Vitamin E toxicity, Wellhealthorganic.com reassures that natural Vitamin E from food is entirely safe. Most adults taking more than the recommended daily amount (22 IU) do so through supplements without reported adverse effects. However, excessive doses, especially above 1000 mg daily, may pose a risk of excessive bleeding, particularly when combined with blood thinners.
Scientific Scrutiny: Controversies and Limitations
Scientists have debated the safety of Vitamin E supplements, with some studies suggesting potential harm. Notably, a meta-analysis of 19 clinical trials, including HOPE and GISSI studies, revealed a higher death rate in those consuming over 400 IU per day. However, these findings come with limitations, and some were based on small studies combining high doses of beta-carotene with Vitamin E.
Also Read : Wellhealthorganic.com know why not to reuse plastic water bottles know its reason in Hindi
Conclusion
In summary, this exploration into Vitamin E covered deficiency signs, potential toxicity, and the diverse health benefits it offers. Well Health Organic’s insights, as shared on Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources , provided a valuable foundation for understanding the significance of this essential nutrient.
FAQs
1. What are the risks associated with excessive Vitamin E intake?
Answer: Excessive Vitamin E intake can lead to stomach distress, nausea, diarrhea, and an increased risk of bleeding, especially for individuals on anticoagulants.
2. How can I boost my Vitamin E intake?
Answer: To increase Vitamin E intake, incorporate foods rich in this vitamin into your diet, such as almonds, hazelnuts, peanuts, and sunflower seeds. If needed, consider natural d-alpha-tocopherol supplements.
3. Can Vitamin E consumption have adverse effects?
Answer: Consuming too much Vitamin E has no recognized adverse effects; however, healthy adults are advised not to exceed 1000 IU per day to avoid potential issues like diarrhea and nausea.
4. What is the recommended daily allowance of Vitamin E?
Answer: The recommended daily allowance of Vitamin E varies by age and gender. For men aged 19 and above, it is 15mg, while for women, it is 12mg per day.
5. How can I determine if I have a Vitamin E deficiency?
Answer: To check for a Vitamin E deficiency, you can request a blood test from your doctor, which analyzes the body’s circulation of this fat-soluble vitamin.